Câu Trực tiếp – câu Gián tiếp là một trong các dạng bài tập xuất hiện khá nhiều dưới ngữ pháp tiếng Anh. Hãy cùng Eng4 tổng hợp các kiến thức ngữ pháp cơ bản và nâng cao về mẫu câu này nhé.
I. Khái niệm Câu trực tiếp, Câu gián tiếp trong tiếng Anh
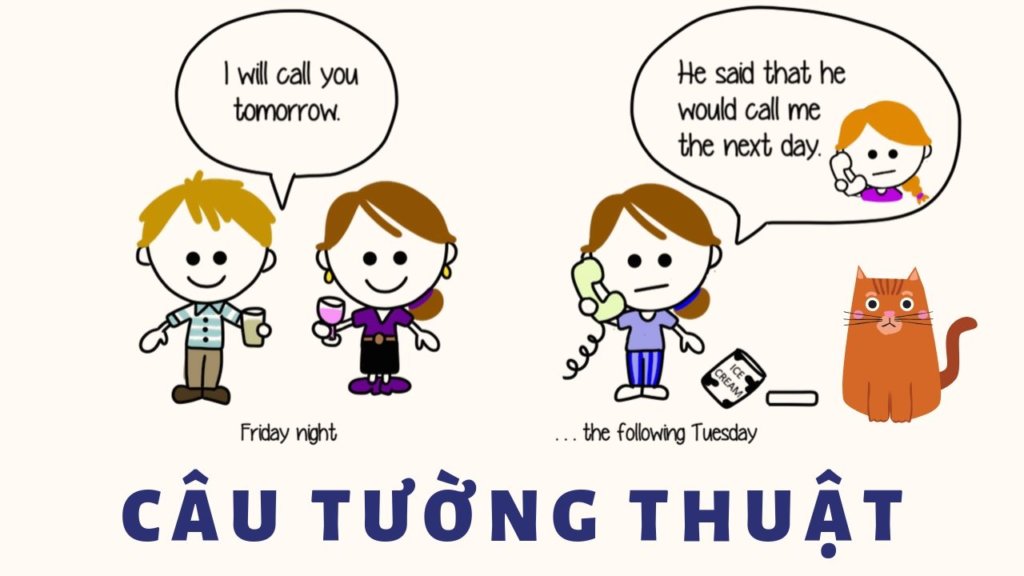
Câu tường thuật là câu thuật lại lời nói trực tiếp.
Lời nói trực tiếp (direct speech): là nói chính xác điều người nào đó diễn đạt (còn gọi là trích dẫn). Lời của người nói sẽ được đặt dưới dấu ngoặc kép.
Ví dụ: She said, ”The exam is difficult”. “The exam is difficult” là lời nói trực tiếp hay câu trực tiếp
Lời nói gián tiếp – câu tường thuật (indirect speech): Là thuật lại lời nói của một người khác trong dạng gián tiếp, không sử dụng dấu ngoặc kép.
Ví dụ: Hoa said, ”I want to go home” -> Hoa said she wanted to go home là câu gián tiếp (indirect speech)
II. Phân Biệt Câu Trực Tiếp – Câu Gián Tiếp Trong Tiếng Anh
Câu trực tiếp (direct speech) là câu nói của người nào đó được trích dẫn lại nguyên văn và thường được để dưới dấu ngoặc kép (“… ”).

Ví dụ: “I love shopping”, she said.
Câu gián tiếp (indirect/reported speech) là câu tường thuật lại lời nói của người khác theo ý của người tường thuật mà ý nghĩa không thay đổi.
Ví dụ: She said that she loved shopping.
1. Câu Trực Tiếp Trong Tiếng Anh
Câu trực tiếp (direct speech) là câu nói trực tiếp của người nói được người viết trích dẫn lại nguyên văn và thường được để dưới dấu ngoặc kép.
Trên 2 ví như trên ta thấy dưới dấu ngoặc kép là lời nói trực tiếp của Lan và Nam và nó được trích dẫn lại một cách nguyên văn
2. Câu Gián Tiếp Trong Tiếng Anh
Để chuyển câu trực tiếp sang câu gián tiếp, chúng ta chỉ cần ghép nội dung tường thuật vào sau động từ tường thuật và thực hiện những biến đổi sau:
a. Cách Sử Dụng Câu Gián Tiếp Trong Tiếng Anh
1. Lùi Thì Của Câu
Nếu động từ tường thuật (reporting verb) của câu tại thì quá khứ thì phải lùi động từ chính về quá khứ một bậc khi chuyển từ lời nói trực tiếp (direct speech) sang lời nói gián tiếp (indirect/reported speech) theo quy tắc sau:
| Câu trực tiếp | Câu gián tiếp |
| Hiện tại đơn | Quá khứ đơn |
| Hiện tại tiếp diễn | Quá khứ tiếp diễn |
| Hiện tại hoàn thành | Quá khứ hoàn thành |
| Hiện tại hoàn thành tiếp diễn | Quá khứ hoàn thành tiếp diễn |
| Quá khứ đơn | Quá khứ hoàn thành |
| Quá khứ tiếp diễn | Quá khứ hoàn thành tiếp diễn |
| Quá khứ hoàn thành | Quá khứ hoàn thành tiếp diễn |
| Quá khứ hoàn thành tiếp diễn | Quá khứ hoàn thành tiếp diễn |
| Tương lai đơn giản | Tương lai đơn trong quá khứ (would/shoud) |
| Tương lai gần | Tương lai gần trong quá khứ (was/were going to) |
| Tương lai tiếp diễn | Tương lai tiếp diễn trong quá khứ |
| Tương lai hoàn thành | Tương lai hoàn thành |
| Tương lai hoàn thành tiếp diễn | Tương lai hoàn thành tiếp diễn trong quá khứ |
Một số trường hợp đặc biệt không lùi thì khi chuyển câu trực tiếp sang gián tiếp:
2. Nếu động từ tường thuật (reporting verb) chia ở các thì hiện tại: chúng ta giữ nguyên thì của động từ chính và các trạng từ chỉ nơi chốn cũng như trạng từ chỉ thời gian trong câu trực tiếp khi chuyển sang gián tiếp.
3. Câu điều kiện loại II và III
4. Wish + past simple/ past perfect
5. Cấu trúc “it’s time somebody did something”
6. Would/ should/ ought to/ had better/ used to không chuyển
b. Biến Đổi Đại Từ, Tân Ngữ Và Tính Từ Sở Hữu
| Câu trực tiếp | Câu gián tiếp |
|---|---|
| I | He/She |
| We | They |
| You | He/She/I/They |
| me | him/her |
| us | them |
| you | him/her/me/them |
| myself | himself/herself |
| ourselves | ourselves |
| yourself | himself / herself / myself |
| yourselves | themselves |
| my | his / her |
| our | their |
| your | his / her / my/ their |
c. Biến Đổi 1 Số Động Từ Khuyết Thiếu
d. Biến Đổi Một Số Trạng Từ Chỉ Thời Gian, Nơi Chốn
| Câu trực tiếp | Câu gián tiếp |
|---|---|
| Here | There |
| This | That |
| These | Those |
| Today | That day |
| Tonight | That night |
| tomorrow | The next day/ The following day |
| Next week | The following week |
| Yesterday | The day before/ The previous day |
| Last week | The week before/ The previous week |
| The day after tomorrow | In 2 days’ time |
| The day before yesterday | Two days before |
| Now | Then |
| Ago | Before |
3. Câu Trần Thuật Gián Tiếp Trong Tiếng Anh
Khi biến đổi câu trần thuật từ trực tiếp sang gián tiếp, chúng ta dùng một số động từ tường thuật: say (that), tell sb (that)
Thực hiện một số biến đổi thiết yếu về đại từ, tân ngữ, tính từ sở hữu,…và lùi thì nếu động từ tường thuật chia tại thì quá khứ.
S + said /said to sb that/ told sb that + Clause
4. Câu Hỏi Gián Tiếp Trong Tiếng Anh

Câu Hỏi Yes/No:
Động từ tường thuật sử dụng: ask, wonder, want to know
Thêm if/whether sau động từ tường thuật
S + asked (sb) / wondered / wanted to know + if/whether + Clause
Chú ý: Nếu trong câu trực tiếp có từ “or not” thì trong câu gián tiếp bắt buộc dùng “whether”.
Câu Hỏi Wh-Questions:
Động từ tường thuật thường sử dụng: ask, wonder, want to know
Sau động từ tường thuật là từ để hỏi và mệnh đề (lùi thì nếu cần thiết) không đảo ngữ
S+ asked (sb) / wondered/ wanted to know + Wh-word + S+ V (thì)
Ví dụ:
5. Câu Mệnh Lệnh Gián Tiếp Trong Tiếng Anh
Khẳng định:
S + asked/ told/ required/ requested/ demanded + O + to V
Phủ định:
S + asked/ told/ required/ requested/ demanded + O + not + to V
Khi câu trực tiếp mang nghĩa ra lệnh, ta dùng động từ tường thuật order:
order sb to do st
6. Một Số Trường Hợp Đặc Biệt Của Câu Gián Tiếp
Đôi khi, tùy vào sắc thái ý nghĩa của câu trực tiếp mà ta sẽ chọn động từ tường thuật phù hợp (ngoài ask, tell), các động từ tường thuật chia làm 2 nhóm chính:
Câu gián tiếp có động từ tường thuật đi với to V
Câu gián tiếp có động từ tường thuật đi với Ving
III. Nguyên tắc cần nhớ khi chuyển từ câu trực tiếp sang gián tiếp
Cụ thể như sau:
| Rule (Quy tắc) | Direct speech (Trực tiếp) | Reported speech (Gián tiếp) |
| 1. Tenses(Thì) | Present simple (V/Vs/es) Hiện tại đơn |
Past simple (Ved) Quá khứ đơn |
| Present progressive (is/am/are+Ving) Hiện tại tiếp diễn |
Past progressive (was/were+Ving)
Quá khứ tiếp diễn |
|
| Present perfect (have/has+VpII) Hiện tại hoàn thành |
Past perfect (had+VPII)
Quá khứ hoàn thành |
|
| Past simple (Ved) Quá khứ đơn |
Past perfect (had +VpII) Quá khứ hoàn thành |
|
| Past progressive (was/were +Ving)
Quá khứ tiếp diễn |
Past progressive/ Past perfect progressive (had +been +Ving) Quá khứ tiếp diễn / Quá khứ hoàn thành tiếp diễn |
|
| Past perfect Quá khứ hoàn thành |
Past perfect Quá khứ hoàn thành |
|
| Future simple (will +V) Tương lai đơn |
Future in the past (would +V) Tương lai trong quá khứ |
|
| Near future (is/am/are +going to+V) Tương lai gần |
Was/were +going to +V | |
| 2. Modal verbs (Động từ khuyết thiếu) |
Can May Must |
Could Might Must/Had to |
| 3. Adverb of place (Trạng từ chỉ nơi chốn) |
This That |
That That |
| These | Those | |
| Here | There | |
| 4. Adverb of time (Trạng từ chỉ thời gian) |
Now | Then |
| Today | That day | |
| Yesterday | The day before/ the previous day | |
| The day before yesterday | Two days before | |
| Tomorrow | The day after/the next (following) day | |
| The day after tomorrow | Two days after/ in two days’ time | |
| Ago | Before | |
| This week | That week | |
| Last week | The week before/ the previous week | |
| Last night | The night before | |
| Next week | The week after/ the following week | |
| 5.Subject/Object (Chủ ngữ/tân ngữ) |
I / me | She, he /Her, him |
| We /our | They/ them | |
| You/you | I, we/ me, us |
IV. Cách chuyển đổi câu trực tiếp thành gián tiếp trong tiếng Anh

1. Quy tắc chuyển từ lối nói trực tiếp sang gián tiếp: lùi một thời
2. Các trường hợp không đổi thì
Sự thật, sự việc luôn luôn đúng:
“The earth moves round the sun” he said. –> He said that the earth moves round the sun.
Câu điều kiện loại II và III:
“If I were you, I would leave here” he said. –> He said that if he were me, he would leave there.
Wish + past simple/ past perfect:
“I wish I lived in Da Nang”, he said. –> He said he wished he lived in Da Nang.
Cấu trúc “it’s time somebody did something”:
“It’s time he woke up”, she said. –> She said it was time he woke up.
Would/ should/ ought to/ had better/ used to không chuyển:
“You’d better work hard” he said –> He said that I had better work hard.
4. Các cách chuyển đổi cơ bản
Say that + a statement –> agree (đồng ý), refuse (từ chối), offer (đề nghị), promise (hứa), threaten + the infinitive (dọa)
Say that + a statement –> accuse …of (buộc tội), admit (thừa nhận), apologise for (xin lỗi), deny (từ chối), insist on + V-ing (khăng khăng)
Say to somebody + a statement –> told somebody + that + clause
“I’ve finished all my homework”, he said to me. –> He told me that he had finished all his homework.
Say + a statement –> said that + clause
“I’m going to Hanoi tomorrow”, he said. –> He said that he was going to Hanoi the next day.
Statement with command, request, advice, invitation, offer –> advise, ask, beg, encourage, invite, order, tell, warn, remind…
Questions in indirect speech
Thời, đại từ, tính từ sở hữu, trạng từ chuyển như ở câu tường thuật.
– Yes-no questions –> asked/wanted to know if/whether
Wh-questions –> asked/wanted to know + question word + clause.
Questions with “shall I…”
–> 4 loại sau:
“Shall we attend the meeting tomorrow”, she said. –>She asked if they would attend the meeting the next day
“Shall I read it, mother?” ha said. –> He asked his mother if he should read it.
“Shall we bring you some new books?” she said. –> She offered to bring me some new books.
“Shall we go to the cinema tonight”, he said. –> He suggested going to the cinema that night.
Questions with “Will you, would you, could you…?” (yêu cầu, đề nghị, mời)–> offer, invite, order, ask, told.
Let’s do…–> suggest + V-ing (nếu bao gồm cả người nói thực hiện hành động)
Let’s do…–> suggest + that S should do…(có thể bao gồm hoặc không bao gồm người nói thực hiện hành động)
“Let’s go to the cinema tonight”, he said. –> He suggested going to the cinema that night. (anh ta cũng đi) –> He suggested that they should go to the cinema that night
Yes, let’s do…–> agreeNo, let’s not do… –> be against the idea.
Must –> had to
Câu cảm thán trong lời nói gián tiếp
What + a + noun/how + adj
–> said that + clause
–> gave an exclamation of d (vui mừng, tán thưởng), disgust (kinh tởm), honor (sợ), surprise (ngạc nhiên)
“Yes/no” –> subject + trợ động từ
“Thank”–> subject + thanked
V. Bài Tập Về Câu Trưc Tiếp và Câu Gián Tiếp Trong Tiếng Anh
Bài 1: Chuyển các câu sau sang câu gián tiếp
- He said, “I like this song.”
- “Where is your sister?” she asked me.
- “I don’t speak Italian,” she said.
- “Say hello to Jim,” they said.
- “The film began at seven o’clock,” he said.
- “Don’t play on the grass, boys,” she said.
- “Where have you spent your money?” she asked him.
- “I never make mistakes,” he said.
- “Does she know Robert?” he wanted to know.
- “Don’t try this at home,” the stuntman told the audience.
- “I often have a big hamburger.”, Benjamin says.
- “If I were you, I’d stop taking tranquizllers. They won’t be good for you health in the long run,” I said.
- Frank: “How much pocket money does Lisa get?”
- “Don’t touch that wire, will you,” said the mother.
- Patricia: “My mother will celebrate her birthday next weekend.”
- “I’m sorry I’m late,” he said.
- “Shall I do the cleaning up for you?” he said.
- “If I were you, I would buy that book ”, she said.
- “Why don’t we go to the cinema tonight?” he said.
- “Would you like to come to my birthday party next Saturday?” she said.
- “Let’s go swimming this Sunday”, he said.
- “ Shall I carry the bag for you?” he said.
- “What a beautiful dress!” she said.
- “How ugly!” he said.
- “Remember to lock the door” she said.
Đáp án
- He said he liked that song.
- She asked me where my sister was.
- She said that she didn’t speak Italian.
- They asked me to say hello to Jim.
- He said the film had began at seven o’clock.
- She told the boys not to play on the grass.
- She asked him where he had spent his money.
- He said he never made mistakes.
- He wanted to know if she knew Robert.
- The stuntman advised the audience not to try that at home.
- Benjamin says that he often has a big hamburger.
- I advised her to stop taking tranquillizers and explained that they wouldn’t be good for her health in the long run.
- Frank asked how much pocket money Lisa got.
- The mother warned the child not to touch the wire.
- Patricia said that her mother would celebrate her birthday the following weekend.
- He apologized for being late.
- He offered to do the cleaning up for me.
- She advised me to buy that book.
- He suggested going to the cinema that night.
- She invited me to come to her birthday party the following Saturday.
- He suggested going swimming that Sunday.
- He offered to carry the bag for me.
- She complimented me on my beautiful dress.
- He said/exclaimed that it was ugly.
- She reminded me to lock the door.
Bài 2: Viết lại các câu sau
1. “Where is my umbrella?” she asked.
She asked……………………………………… ………………….
2. “How are you?” Martin asked us.
Martin asked us………………………………………… ……………….
3. He asked, “Do I have to do it?”
He asked……………………………………… ………………….
4. “Where have you been?” the mother asked her daughter.
The mother asked her daughter…………………………………… …………………….
5. “Which dress do you like best?” she asked her boyfriend.
She asked her boyfriend………………………………….. ……………………..
6. “What are they doing?” she asked.
She wanted to know………………………………………. …………………
7. “Are you going to the cinema?” he asked me.
He wanted to know………………………………………. …………………
8. The teacher asked, “Who speaks English?”
The teacher wanted to know………………………………………. …………………
9. “How do you know that?” she asked me.
She asked me………………………………………… ……………….
10. “Has Caron talked to Kevin?” my friend asked me.
My friend asked me………………………………………… ……………….
Đáp án
- She asked where her umbrella was.
- Martin asked us how we were.
- He asked if he had to do it.
- The mother asked her daughter where she had been.
- She asked her boyfriend which dress he liked best.
- She wanted to know what they were doing.
- He wanted to know if I was going to the cinema.
- The teacher wanted to know who spoke English.
- She asked me how I knew that.
- My friend asked me if Caron had talked to Kevin.
Chúc bạn học tập tốt và ôn luyện thi TOEIC hiệu quả.